
In the Group Statistics box, the table shows the number of elements/subjects in each group/treatment level, together with the mean and standard deviation of the dependent variable for each group. In the same tab, the input is grouped and shown as a table, on the right side of the screen. score of a test carried out on the subjects.
#Anova calculator f free
In our case, it represents the Free Thyroxine level in the blood. In the “Dependent Variable Name” and “Dependent Variable Values” boxes, input the data for the dependent variable. For example, we could have inputted the factor levels as “Drug1”, “Drug2”, “Drug3” and “Drug4”. Note that the app also accepts text instead of numbers in the “Factor Name box”. In our example the factor is “Drug” and its categories are “1”, “2”, “3” and “4” representing four different types of drugs produced by a pharmaceutical company. Note that the factor should have at least 3 distinct categories (known as factor levels). Input the name of the independent categorical variable in the “Factor Name” box and the category of each subject in the “Factor Values” box, separated by “,” or “ ”. The model accepts one independent categorical variables known as factor, and one dependent continuous variable. The sidebar of the Input tab contains the input for the one way ANOVA model.
#Anova calculator f how to
How to use and interpret the One Way ANOVA calculator and dashboard Input tab 05), we can reject the null hypothesis of the ANOVA and conclude that there is a statistically significant difference between group means.Free Online One Way ANOVA Calculator and Dashboard If the p-value is below a certain threshold (e.g.The higher the F-value, the lower the corresponding p-value.The higher the F-value in an ANOVA, the higher the variation between sample means relative to the variation within the samples.The F-value in an ANOVA is calculated as: variation between sample means / variation within the samples.Here’s a brief summary of the main points in this article: In other words, this tells us that the variation between the sample means is not high enough relative to the variation within the samples to reject the null hypothesis. This means we don’t have sufficient evidence to say that the studying technique used causes statistically significant differences in mean exam scores. 05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Upon performing a one-way ANOVA for this dataset, we find that the F-value is 2.358 and the corresponding p-value is 0.1138. The variation between the samples is represented by the differences between the sample means: The variation within the samples is represented by the spread of the values within each individual sample: We can create the following plot to visualize the exam scores by group: The following table shows the exam scores of 10 students who used each technique: Suppose we’d like to perform a one-way ANOVA to determine if three different studying techniques produce different mean exam scores. To gain an intuitive understanding of the F-value in an ANOVA table, consider the following example.
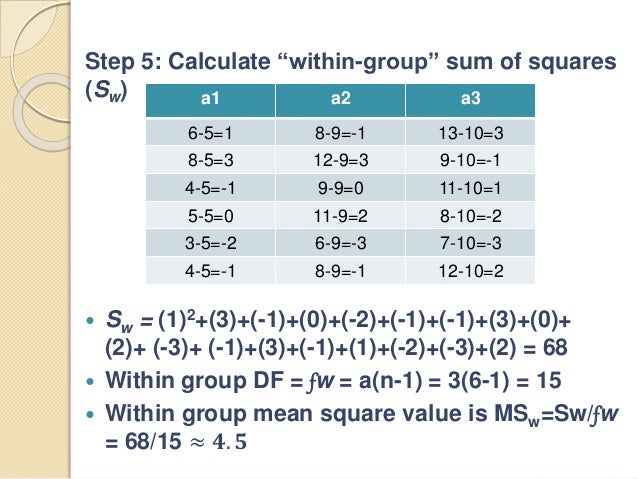

This means there is no statistically significant difference between the means of the three groups. To find the p-value that corresponds to this F-value, we can use an F Distribution Calculator with numerator degrees of freedom = df Treatment and denominator degrees of freedom = df Error.įor example, the p-value that corresponds to an F-value of 2.358, numerator df = 2, and denominator df = 27 is 0.1138. If the variation between the sample means is high relative to the variation within each of the samples, then the F-value will be large.įor example, the F-value in the table above is calculated as: F-value = variation between sample means / variation within the samples.F-value = Mean Squares Treatment / Mean Squares Error.The F-value in the table is calculated as: Whenever you perform a one-way ANOVA, you will end up with a summary table that looks like the following: Source H A: At least one group mean is different from the rest.A one-way ANOVA is used to determine whether or not the means of three or more independent groups are equal.Ī one-way ANOVA uses the following null and alternative hypotheses:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
